It seems that this subject is a lingering question to many of the readers of dipole gravity. When a new metric is devised, this certainly becomes an important issue. A fully covariant field equation was expanded in the linearized theory and expressed by sums of infinite number of the individual multipole components. So in reality, the individual poles(monopole, dipole, quadrupole...etc) are not covariant by themselves, the total sum is. In other words. dipole gravity can be formulated only in the asymptotically flat space time region. However this argument can not be used to underestimate the importance of its physical implication. Just like Newtonian gravity is a solution of general relativity in the asymptotically flat space time region, so is dipole gravity. The most important aspect of it may be its unique topology.
Even so, it is amazing to see how much of the cosmological mysteries are solved solely by Newtonian(monopole) gravity. As the energy scale of the cosmological system gets larger, the higher order of the poles start making important contributions. The reason Newtonian gravity could not explain the jets and/or the dark matter problem was, in retrospect, because we have been working with a totally simplified, truncated non covariant field. As the more of the higher order poles are included, the overall gravity field starts becoming more accurate and offer solutions to many other mysteries of the universe. Since the strength(magnitude) of the each poles decrease by the factor of c (speed of light) as the order increases, after the inclusion of the second and third terms of the linearized theory the overall sums of the field will still be accurate enough to cover most of the observable universe.
So, one can view the overall scheme of the linearized theory of general relativity by the following; the spatial translational motion is covered by Newtonian gravity(via point mass approximation), the intrinsic rotational motion of the bulk object is covered by dipole gravity and finally the intrinsic vibrational motion of the extended object is covered by the gravitational quadrupole moment.
In retrospect, I always felt that there was something fundamentally missing in our understanding of the universe. I remember looking up the text books on gravitation in 1982, even though I was not an astronomy major when I was a graduate student at the University of Michigan Ann Arbor. I was interested in the theoretical high energy physics. The most puzzling experience in this episode was when I looked up the page describing the linearized form of general relativity. There was something next to Newtonian gravity and that was the dipole gravitational moment. And it was dismissed by a reason that I thought was too much of tongue in cheek argument. The fact that one has to move the origin of the coordinate system to the center of mass of the object to remove the term seemed too convenient or/and unnatural(can't find the right word for it) because one can always set up the origin of the coordinate system at the center of mass of the object and forget about the coordinate alignment problem. I thought it was an unnecessary and non physical activity which may hide some more serious physics involved. The reason for its dismissal, I thought, was too frivolous compared to the possible importance of the term.
Because if general relativity have answers to the further mysteries of the universe, it should be in the term next to the Newtonian gravity in the linearized theory.
The conventional treatment of it made me feel suspicious of the argument. I never trusted any derivation of the physical equations in the text books in my college years until I derived it myself anyways.
It's like weighing a feather same as a gold nugget painted like a cotton.
But there was no way I could have guessed at the time that it could have something to do with the anomalous center of mass shift from the rotating hemisphere. In 1995, the puzzle was solved after 13 years since I began wondering about the strangeness of displacing the origin of the coordinate system to remove the dipole term in the linearized theory. It happened when I asked the following two questions in my mind. What is so special about the rotating hemisphere? And then how about the center of mass? The answers to these two questions answered the 13 years old questions in my mind. Hermes struck me down at the instant. The gravitational dipole moment!!!! It looks like there is no way one can avoid this solution. The jets and the dark matter problem are the two different sides of the same coin due to the dipole gravity effect from the fast rotating black holes.
At the moment, the quadrupole gravitational moment seems to be the main interest of experimental investigation in gravity. However, we missed dipole gravity altogether and there is no doubt that it should be investigated fully in the near future especially because it is much more stronger than the quadrupole moment. The extensive investigation of dipole gravity will determine the scope of the overall success of Einstein's initial revolution.
After that, when we still have too many mysteries remain unsolved, the next order of the poles will offer important clues to the problem. In this respect, the quadrupole moment will become important in the much high energy scale than that of dipole gravity, so we may be too far ahead of our steps in the adventure to the cosmological mystery.
In regard to this subject, if we assume that a big bang occurs in a much higher energy scale than that is governed by dipole gravity, it is quite conceivable that the instability arising from the vibrational oscillation of the quadrupole moment can result in the massive disintegration of the black hole in the form of a big bang. So, the extreme relativistic extension of the gravitational quadrupole moment can be a big bang which is listed as a question mark(?)in the dipole gravity chart.
Theory of Gravitation, Cosmology and a part of general relativity
Sunday, December 30, 2007
Questions on the Covariance of Dipole Gravity
Thursday, December 27, 2007
How to Falsify Dipole Gravity?
There may be several ways to theoretically dispute the validity of dipole gravity.
1. There is no mass increase effect due to special relativity.
2. There is no ideal solid object in relativity theory.
3. Hemisphere may deform while in rotation so that it may cancel the shift of the relativistic center of mass.
4. Relativistic shift of the center of mass has nothing to do with the dipole gravitational moment in general relativity.
5. There may be dipole gravity effect but the spherical shape of the source will completely cancel the effect.
6. Ehrenfest paradox negates the effect of the relativistic center of mass shift.
The statement number 1 is a false. The special relativistic mass increase effect has been observed and confirmed. The statement number 2 has been discussed in the paper "Non Newtonian force...." In fact, the question of the rigidity must be considered a relative one. Depending on the binding force of the dense stellar object, the degree of rigidity will vary. The statement number 3 can be disputed by the fact that, in general, the longitudinal asymmetry is all it needs to have a shift in the center of mass of a rotating object, so the deformation itself doesn't affect the fact that it will have a shift of the center of mass. The statements number 4 and 5 can be disputed by the fact that dipole gravity reproduced the exact form of the Lense-Thirring force at the center of the rotating spherical shell.
Now regarding the statement number 6, some readers of the dipole gravity article objected to the notion that there is a relativistic center of mass shift for a rotating hemispherical rotor by invoking Ehrenfest's paradox, which states that due to the length contraction effect of special relativity, the circumference of a rotating ring will be shorter than given by 2piR(the length of the radius will still be the same).
So the mass of the rotating ring should be the same regardless of the speed of the rotation according to their objection.
However, if we assume that the ring is made up of N number of atoms connected in series, each atoms will experience the special relativistic mass increase effect, and since the number of the atoms can not change due to the rotational motion, the relativistic mass increase effect for the whole ring(as well as for the whole hemisphere) should still be effective.
The next objection is from the simple comparison with the electromagnetic phenomenon. The electricity and magnetism has electric and magnetic dipole moment because there are two different charges in the theory of electromagnetism, ie, positive and negative charges of electricity and north and south poles of magnetism, but there is no negative mass in gravity so how can you have gravitational dipole moment?
While gravity and electromagnetism are both long range forces, they are fundamentally different forces of nature. In fact, the fact that there is no observed negative mass in the universe has contributed greatly to the notion that there should be no gravitational dipole moment in the physical world. However, general relativity in the linearized form only requires a physically meaningful shift(not the kind that can be eliminated by a coordinate translation) of the center of mass, not the presence of a negative mass for the existence of a gravitational dipole moment.
The question on why this shift implicated in the linearized theory of general relativity should be identified with the relativistic shift of the center of mass of a rotating longitudinally asymmetric object may be entirely a matter of faith. There is no reason it should be identified as such. But then there is also no reason it should not. At least it confirmed the result calculated by a different method of analytic integration performed by Lense-Thirring.
As in the Dirac's equation of the relativistic theory of positrons, a mathematical equation can be interpreted by predicting a certain new physical reality.
The entire justification of such an interpretation totally remains in its predictive power of the physical nature.
So the last resort to falsify dipole gravity remains in the test of its fundamental predictions since all the features of the dipole gravity potential have been consistent with the observed cosmological data.
Newtonian gravity started from the conceptual extension of the force that was observed from a falling apple(the real story behind will be much more complicated and deeper than can be described by such a simple story), the same force is exerted in the planetary system as well as in our daily lives. It seems clear that the massive cosmological phenomena like the jets and the dark matter problems should have a similar counter part in our daily lives so that we can observe it. Since dipole gravity is the second order effect from general relativity, its strength should be much weaker than Newtonian gravity and as such its effect will be much harder to detect in the terrestrial environment. But it is certainly within our current technological reach to test it as shown in the previous pages.
What if the test disproves the prediction?
I think it is possible, but it will ultimately mean a disproof of general relativity.
Tuesday, December 25, 2007
Rocketless Propulsion by Dipole Gravity
The theoretical explanation of the mysteries in cosmology may be the least exciting part of the consequences of dipole gravity. Apart from the obvious engineering difficulties associated with finding materials that can withstand the enormous centrifugal force that can tear up the whole structure of the rotor, dipole gravity is a practical and efficient method of propulsion in space travel.
Once a certain level of rotational speed of the dipole rotor is reached, it will start propelling the ship with an ever increasing speed without any additional expenditure of energy according to the theory of dipole gravity. The ship travels in space like falling down a constant gravity field except that there is no fixed source of a gravity center. The ship propelled by dipole gravity will travel the space like sliding down hill as it creates its own slope of the hills which depends on the rotational frequency of the dipole gravity rotor.
In theory, there is no limit of the speed of travel in this propulsion method.
What happened to special relativity that limits the speed of travel to the speed of light?
Special relativity applies when there is no curvature in space time, meaning when there is no gravity field. In terms of the tachyonic world picture, it means in the region where the density of the tachyonic neutrinos are uniform. Motion in space in this mode is like that of running against the blowing wind, not with the wind. The atomic nuclei of the material in motion in this mode suffers dislocation and huge resistance due to the enormous collision with the tachyonic particles. This is the main cause of the increase of energy(mass) as the object travels faster and faster in space by Newton's third law of motion. Any living organisms will not be able to withstand the stress without getting destroyed. The integrity of the structure of the material is not supported in this mode of travel as the speed gets close to the speed of light.
However, in the mode of the dipole gravity propulsion, the ship is enveloped inside the tachyonic aether's clothing. The ship is naturally following the density gradient of the spacetime curvature itself. In other words, the front side of the space of the dipole gravity propulsion device is an artificially created aether vacuum while the back side of it is a compressed aether space.
Alcubierre devised a metric that resembles this configuration in spacetime.
So, in the dipole gravity propulsion scheme, the imbalance of the surrounding tachyonic aether pressure is the one responsible for the acceleration of the ship itself. So the nuclei of the material inside the aether gradient doesn't suffer the massive pressure against the tachyonic neutrinos. The ship is traveling fast, even faster than the speed of light, but there is no increased aetheric pressure associated with it and thereby the structural and biological integrity of the ship is preserved.
After all, the black hole is a blob of space where tachyonic neutrinos can not penetrate. In a sense, it is a gigantic localized aether vacuum where all the material objects close to it are bound to fall into.
It's no suprise that the extreme relativistic extension of dipole gravity becomes a one way transversabe worm hole while that of Newtonian(monopole) gravity a black hole.
Friday, December 21, 2007
The Length of the Jets from Dipole Gravity
The lengths of the jets are determined by the peak of the repulsive dipole gravity potential on both poles of the rotation axis. The strength of dipole gravity falls more rapidly than the Newtonian gravity, so at certain point of the distance from the center, the attractive force of Newtonian gravity will dominate over the repulsive force of dipole gravity, which is the cause of the return trajectory and the brightly lit jets observed from the black hole accretion disks. 
Essentially, the property of the linear trajectory is a function of the rotational frequency, total mass and the geometrical shape of the galactic core which determine the magnitude of the length element of the relativistic center of mass shift. Since the geometrical shape of the core can not be determined apriori, and also since its observation is out of the reach of the currently known method, the gravitational dipole moment will need to be treated as an adjustable parameter. One can assume a certain shape for the core, its mass(density as well) and the rotational frequency to estimate the actual length of the jets. It is noted that the length of the jets are very sensitive to the peak height of the repulsive dipole gravity potential. Due to the thermal fluctuation of the molten core material before the ejection, it is expected that there will be corresponding fluctuations on the length on the jets and also on the population density of the dark matter halo. The estimated dark matter population density function predicted by dipole gravity is 1/r. However, this density function suggests an infinite wise distribution which can not be true. So at certain point at the far out distance, the density distribution function is expected to decrease more rapidly than 1/r, because the density distribution can not suddenly be truncated to zero at distance r=ro(ro is the distance where the density distribution deviates from 1/r). In this sense, NFW's proposal of 1/r^3 dependency on the density distribution beyond certain distance limit r=ro is justified. (I'm indebted to Prof. Joel Primack for providing me with this information).
It would be interesting to see if the property of the thermal distribution of the molten core material could be related to the 1/r^3 dependency in the population density of the dark matter halo at the far out stretch as the compressed molten material would not all have the same kinetic energy at the peak height of the repulsive dipole gravity potential.
Wednesday, November 21, 2007
Farce of Quantum Gravity
The Michigan nobel laureate Dr. Martinus Veltman who is a great teacher and also a man of great inspiration in high energy physics used to note in the class that quantum gravity has not been found to be renormalizable. If a quantum field theory is not renormalizable, its prediction can not be considered reliable. It basically means that quantum gravity is not a viable physical theory.
There can be several reasons for this. First and the foremost possibility is that gravity may not be a quantum phenomenon after all as I mentioned in the previous pages. Dipole gravity strongly suggests that gravity must be a bulk effect. If gravity is not a quantum phenomenon, any attempts to unify gravity with other forces of the nature will be fruitless.
It may not be a coincidence that quantum gravity hasn't provided a single testable predictions in the atomic level other than the quantum wormhole that no one knows how to create one. Also, I do not understand why quantum worm hole should be relevant to the macroscopic world even if it may exist in some kind of an unknown form.
I think the physics world has been pushed too far into letting believe plausible nonsenses that when the real physical theory came out, no one seems to be able to figure out what the real truth was or has been.
Physics is a discipline where you have to be able to mechanically imagine the situation no matter how complex the system may look like. Without the intuitive mechanical guidance, physics becomes a meta physics where no one knows for sure how the world is exactly operating.
When the quantum wormhole theory came out and the very concept was used as a main theme of a scifi movie, I was wondering if we are being totally detached from the common sense in a massive scale.
The current culture of physics is that if a calculation shows the correct result, with an accuracy of 10^-10 order, that should be enough for the validity of a physical theory that predicts it. It doesn't matter if the theory is mathematically or mechanical intuitively faulty.
The very fact that one has to subtract infinities from the calculation to make sense out of the theory is purely a mathematical nonsense. But for physicist it doesn't matter as far as the result justifies the means.
At this point, one should feel that there must be much more to it than quantum field theory in the world of physics.
Tuesday, November 20, 2007
Shrunken Degree of Freedom of Motion
Newtonian mechanics has taught us that an extended object in space has six degrees of freedom of motion. That is because there are three spatial degrees of freedom of translational motion and the additional three degrees of freedom of motion by spin rotation. Those six degrees of freedom of motion do not depend on one another within Newtonian mechanics.
Now one can see that dipole gravity tells us that is not exactly the case. An object which has the longitudinal asymmetry like a hemisphere has the degree of freedom of motion gets entangled because the spinning along the symmetry axis causes the voluntary motion along the same axis.
Of course, this happens only when the object is not of spherical or cylindrical shape. One may wonder if this can have any implications on the kinetic theory of gases because some molecules have tetrahedral shape which is longitudinally asymmetric no matter which direction it may want to spin rotate. There have been reports of anomalous behavior on the specific heat coefficient on gaseous states of some of the molecules.
I want to draw attention of the experts in the field onto this phenomenon. We may have an additional proof of dipole gravity in action in the microscopic level. Obviously the universe is not exactly the way we used to think it should be. Instead of six degrees of freedom of motion, we may have only 5.5 degree of freedom of motion. Considering that people are talking about 10 dimensional space according to the string theory, this idea of shrunken degree of freedom of motion may not be too far fetched.
Obviously there are ways to develop a theory in physics by going up the higher order of symmetry into which everyone is involved to get an answer but there are also ways by following the direction of broken symmetry which is the case of dipole gravity. By observing the way how the symmetry is breaking in physics, it can guide us to the answer to many of the unsolved mysteries in the universe.
Thursday, November 8, 2007
Possible Cause of Gamma Ray Bursts
The static quadrupole (two superposed dipole) gravity force field from the fast rotating compact stellar object can produce dipolar gravity orbits of the stellar particles totally unlike that of Newtonian gravity. The complexity and the diversity of their orbits can be quite interesting.
Due to the integrated effect of the orbit from the force line, one can expect the equatorial plane of the fast rotating black hole like dense stellar object will be a massive battle ground of the violent collisions of the particles coming from both poles of the rotation axis of the rotating star in the opposite direction.
Those particles will not smoothly join together to fall into the equatorial center of the black hole. The momentum accumulated while traveling toward the equatorial plane will make them to pass over the plane and cause them to make violent collisions. The static quadrupole gravity potential predicts that there will be oscillatory trajectories across the equatorial plane increasing the chance of impact until they lose all the kinetic energy in the longitudinal axial direction, which is basically the cause of the alignment of the debris in the equatorial plane of the rotating black hole.
The chance of the collision will depend on the volume density of the debris ejected from the poles. While most of them will be either small scale collisions producing insignificant level of gamma rays or miss entirely, it is quite probable that some of them will hit each other head on with huge impact.
Some of those collisions can be so strong and violent due to the sheer size of the debris and the speed of travel that it will register in the earth telescope as giant gamma ray bursts. Studying the location and the frequency of these collisions will help solve the mystery of the galactic centers.
Also another strong possibility is that the collision of the large size debris into the center of the black hole itself can be the cause of the gigantic gamma ray bursts because that is the final destination of the matters composing the dark matter halo. While they are still invisible due to the lack of a stable orbit and the enough time for the nucleosynthesis, the sheer size of them colliding into the center of the galaxy will generate huge amount of gamma ray bursts.
Another interesting related possibility is that there can also be parasitic orbits circling around the dipole gravity force lines near the poles like that of an angel ring on top of a saint's head where the dipole gravity force is the strongest. And some of them may have already been observed.
Tuesday, November 6, 2007
Why MONDian Cosmology is Wrong?
It is not in what the theory explains. It is in the fundamental assumption the theory is based on. MOND demands the Newtonian dynamics to be modified in the large scale universe. However, Newtonian mechanics has been proven to be correct from the microscopic atomic scale to the macroscopic scale of the solar system. There is no compelling reason it should not work and need to be modified in the large scale universe since it has never been proven to be incorrect in any other branches of physics. And the assumption doesn’t seem to shed any new lights on any other major cosmological problems.
Furthermore, the problem is not only in their assumption, but also in the missed understanding of the additional long range gravity force that has been eluding the physics community for a long time. Typically known as the tidal gravity force is a conceptually misunderstood force that has never been mathematically formalized but thought to exist if the equivalence principle is assumed to be correct on which general relativity is fundamentally based.
The fact that Lens-Thirring force could be derived from dipole gravity force indicates that Lens-Thirring, tidal gravity, the gravito-magnetic forces are fundamentally the many different manifestations of the same dipole gravity force resulting from the rotation of a longitudinal axially asymmetric object like a cone or a hemisphere due to the component wise accumulation of the acceleration induced gravity force.
A theory starting with a totally unjustified assumption and with the missed long range gravity force can not be correct even if it may explain anomalous galactic rotation curves.
The more serious problem with the theory may be on what it doesn’t explain. The jets from the black hole accretion discs and the planet Saturn mystery seem to have nothing to do with MOND.
Of course, one can always argue that MOND was not meant to explain the jets nor the planet Saturn mystery but obviously that's a self defeating argument because dipole gravity was not even meant to explain anything other than finding its own place in general relativity.
Friday, October 26, 2007
Returning to the Mechanical Universe
In some sense, the development of quantum mechanics and quantum field theory in the early 20th century has blurred the intuitive nature of the physical world because the probabilistic interpretation of the subatomic particles has been proven to be so accurate. But the question of what is the true nature of such a probabilistic universe has not been asked seriously enough. It seems like the key to the hint was in the mysterious properties of the neutrinos.
If we assume that Einstein's theory of special relativity represents the reality in both the inside and the outside of the light cone, the problem becomes very simple. We have astronomical number of particles traveling faster than the speed of light and their mass is represented by imaginary numbers.
People may say it is a nonsense. But it may be the nature's way of telling us that the universe has more than just massive particles and photons.
What it tells us is that there are particles traveling faster than the speed of light and they are neutrinos. The beauty and the simplicity of this concept are beyond imagination.
First of all, the Lorentz invariance is not violated. The mystery of the negative mass squared problem from the multitudes of experiments for the neutrinos are solved. The question of why the neutrinos were detected earlier than the actual visual observation of the supernova became trivial.
There is no problem of explaining how and why lights can propagate through the absolute vacuum. If those fast traveling tachyonic neutrinos are pervading the universe, in a way, they are the real permanent residents of the universe, the material worlds are just temporary drifters.
They act up the electrons around the atomic nuclei and make them behave the way they are in the physical world. Quantum mechanics is only one of the many mathematical ways to predict the nature of atomic world. The probabilistic nature enters into the picture because the universe is populated by the random yet very homogeneous density of the tachyonic neutrinos.
It will be easy to understand the picture by imagining how the individual air molecules are behaving in the atmospheric pressure. They try to preserve the pressure equilibrium in the space as the tachyonic neutrinos will behave the same way in the universe except that those particles are moving so fast that it doesn't take long time to get to the point of a constant equilibrium of the homogeneity.
Monday, September 3, 2007
Planet Saturn Mystery and Dipole Gravity
If one throws rocks in random direction toward the planet Saturn with a certain initial orbital angular momentum, the rocks will form stable orbits exactly defined by the initial angular momentum and the Newtonian gravity. There is no other gravity force within the conventional gravitational physics that forces the rocks to align perfectly around the equatorial plane of Saturn.
The observed distribution of the debris suggests that there is a force that makes them to prefer stay in the equatorial plane as if there is a gravitational potential dip around the equatorial plane as suggested by dipole gravity.
The holes in the poles of Saturn are also startling. It looks like a precursor of the poles emitting jets. There must be a force that does not allow materials to stay in the column of the polar axis.
If there is a very fast rotating high density core inside the Saturn cloud, dipole gravity can make it possible. Even if the repulsive force may be weak, the polar columns can remain hollow. In many different senses, Saturn look like a miniature, watered down form of dipole gravity model mainly due to the possible existence of the fast rotating core inside the planet. The shape of the ring suggests that the radial dipole gravity force is very short ranged in such way that the orbits of the ring materials remain stable for a long time.
Simple computer simulation of the dipole gravity model will predict the Saturn style formation of the rings and the polar holes without too much difficulty.
Tuesday, August 7, 2007
Dipole Gravity Charts

Anomalous relativistic center of mass shift breaks the Newton's second law of motion which in turn causes the dipole gravity effect in general relativity. As expected, dipole gravity is completely non-Newtonian, suggesting the possibility of the motion without the explicit external force in the direction of the movement.
Typically known as the tidal gravity force, frame dragging force and the gravito magnetic force are degenerated forms of dipole gravity force all known by their own source of justification without the unified understanding of their origin.
The following chart shows the hierarchy of the gravity forces in general relativity including dipole gravity. In the strong field regime, each forces exhibits singularity behavior. However, we do not know yet what the quadrupole gravitational radiation will be like.

Sunday, July 29, 2007
Comments on LIGO/LISA and Dipole Gravity
It may not be off the mark to state that the current major paradigm of science is still defined by Newtonian mechanics. Momentum is conserved when there is no external force that compels the motion of the object in the direction of the movement as well as the energy that is within the moving object. Thermodynamics, known Electromagnetism and all other major physical disciplines do not circumvent this major paradigm of the presently known scientific doctrine. Please note that I intentionally put “known” in front of Electromagnetism because I noticed there is also a remarkable anomaly within Electromagnetism itself that also seriously challenges this well known paradigm.
If anyone has noticed, the discovery of dipole gravity in general relativity means that the major challenge to this paradigm has begun. It proposes a major mechanical system that can break the three hundred year old paradigm of physics. Basically what it means is that the local energy momentum is influenced by some unknown energetic particles in the universe in such a way that one can devise a specific mechanical system that can funnel the background energy into the local arena.
When an ultra compact stellar object rotates fast, this is exactly what is happening in the surrounding area of the rotating star in such a way that the jet streams gain tremendous amount of energy while being ejected. Within the paradigm of dipole gravity, this is natural and inevitable.
To corroborate this observation, the astounding energy efficiency factor of the jets has been studied and reported in the recently published paper by Steve Allen and Christopher Reynolds.
Then the next question is “what do we gain by proving the existence of the quadrupole gravitational radiation by spending billions of dollars?” “What kind of industrial benefit would it produce?”
First off, its detection would not produce any result that may challenge the existing paradigm of science although it may provide one more test that proves general relativity is a correct theory of the universe.
Secondly, I seriously doubt if there will be any tangible industrial applications or benefits of the result since the system involves astronomically massive objects to produce the quadrupole gravitational radiation effect.
In science fiction story, one could easily argue that one can have a very different communication technology using the quadrupole gravitational radiation. However, in terms of the available energy scale, this will be hardly practical.
Would it be a waste of money, time and energy?
I wouldn’t necessarily call it that way before there were no other alternatives. But now when the new test of general relativity is proposed and available, a part of the effort of LIGO/LISA can be used to test dipole gravity predictions because it costs much less and the impact of the result can be significant in all aspect of our lives.
Tuesday, July 17, 2007
Necessity for the Revision of the Text Books on Gravitation
It is also obvious that there is nothing much to debate about its reality. It's like looking at your five fingers in your own hand, if anyone had a decent amount education in physics.
Then, why the gravitational physics community is so quiet about this discovery?
It could be a shear disbelief, dumbfoundedness and despair, I suspect.
The logical consistency of the theory is crystal clear that it can not be disputed. That's the reason there is not a single attempt to dispute the validity of the theory.
It basically marks the end of the game of the pursuit in search of the ultimate mechanical secret of the universe where the last part of the emotional despair could come from among the researchers in the field because we all know there can not be more than one truth.
While this theory may mark the end of the pursuit game, it also signals the beginning of the new scientific era in human society.
I think it's time to seriously discuss the necessity of performing the test of the predictions of dipole gravity.
The benefit of the scientific advancement due to this knowledge to human society will be astronomical.
Sunday, July 1, 2007
Implications of Dipole Gravity
"Despite Einstein's proposal of three classical tests, the theory was without strong experimental support until a program of precision tests was started in 1959. This program has systematically tested general relativity in weak gravitational fields and severely limited possible deviations from the theory. Since 1974, Hulse and Taylor have studied stronger gravitational fields in binary pulsars. In these regimes, on typical solar system scales, general relativity has been extremely well tested. On the largest scales, such as galactic and cosmological scales, general relativity has not yet been subject to precision tests. Some have interpreted dark matter and dark energy as a failure of Einstein's theory at large distances, small accelerations, or small curvatures."
There is no denying that there have been general sentiments that (currently known) general relativity has not been fully successful in predicting cosmological events at large scale and small accelerations.
This is one of the major reasons we have the theory of MOND and the dark matter hypothesis (which turns out to be correct) to explain the flat rotation curves. If dipole gravity in general relativity had been discovered earlier, we wouldn't be struggling with these problems unless it became absolutely clear that dipole gravity could not explain any of those cosmological problems. It simply reflects the level of confidence physicists have in general relativity today.
If there is a reason that the dark matter could not be made of any other exotic matters, it would be because it is difficult to explain why such an exotic matter should exist there but not here around us if the universe is homogeneous and isotropic.
Dipole gravity is a totally new form of an additional long range gravitational force which is comparable to Newtonian gravity and other three forces, ie, Electromagnetism, Weak and Strong forces, of nature.
One of the most exciting features of dipole gravity is that it shows us the totally new kind of propulsion method to travel the universe. In a sense, it gives matters in the universe the freedom to move around not only in the radial or circular direction around the stars but also in any possible directions in such a way that, for instance, the motion of the bullet clusters can be possible without contradiction.
Dipole gravity is not specifically designed or created to explain the jet phenomenon or the dark matter problem. It came out of the dissatisfaction of the known theory of gravity while there are so many unexplained mysteries in the universe. It is rather a reclamation of the forgotten or, one may say, mistakenly abandoned physics in general relativity.
In lay man’s term, dipole gravity, if verified by experiment, means we are on the verge of the next Scientific Revolution.
Sunday, June 24, 2007
What is the Major Mathematical Equation of Dipole Gravity?


The parameter etha in equation (17) is necessary to smooth the mathematical artifacts of the singularities at the distance R/2 and -R/2 along the Z direction, which are the center of mass of the individual hemispheres in the rest frame and V(r) is the Newtonian gravity from the rotating spherical shell.
The above functional expression is the three dimensional dipole gravity potential which is responsible for the jets and the dark matter problem. It is noted that this dipole term doesn't exist in the traditionally known theory of general relativity. The jets and the dark matter problem are two different sides of the same coin of dipole gravity. One can not be explained without the other. Numerical simulation and the various curve fitting will start from the equation above. The information related to the rotational frequency and the longitudinal asymmetry of the object is contained in the parameter representing the gravitational dipole moment dz/2, where dz is given by the total mass M times delta rc.

where R is the radius of the rotating spherical shell and c the speed of light for a slow limit of rotational frequency(v/c<<1). For a fast rotational frequency, the following expression can be used for the shift of the center of mass which applies to the rotating spherical shell.


However, in most of the applications, it would be difficult to tell if the core of the rotating galaxy can be represented by a spherical shape or by something totally different. Regardless of the detailed shape, the rotational frequency and the asymmetry(asymmetricity) of the geometrical configuration of the source is reflected in the gravitational dipole moment dz. Hemisphere is only one of the many possible geometrical shapes that can create gravitational dipole moment. The importance of the dipole gravity potential may be in the overall topological consistency, when it comes to the explanation of the large scale cosmological problems, which means if the functional form has all the necessary coordinations to predict the correct results.
Sunday, June 17, 2007
Response to Questions from Colleagues(On the Covariance of Dipole Gravity)
Is the theory covariant? Does it account for gravitational lensing? Can it explain the bullet cluster? These are all the sorts of questions people are probably asking you. I'm sure you have answers.
Best wishes,
daniel
Hi Daniel,
Thanks for your email with the questions. Let me try as best as I can. If you ask if Newtonian gravity is covariant, the answer will be no. Probably it's the same with dipole gravity. It's just a linearized weak field limit solution. But one may try to formulate a specific tensor metric to study the strong field regime of dipole gravity and then the question of covariance will become important. Just like Newtonian gravity becomes a black hole in the strong field regime of Schwarzschild metric, the result will be a predictable extension from the weak field limit behavior. One possible reason that it may be hard to find a tensor metric for dipole gravity will be that it is not a stable gravitational system. The system will not be local. In other words, in the strong relativistic field regime, the gravitational dipole moment will not be at the local spot where one expects it to be because of the extremely strong accelerating force it experiences from the rest of the universe. Theoretically, in such a case, how one can devise a tensor metric where the acceleration can be so strong that the locality of the system can not be well defined. If it is a moving system with a constant speed, it will be trivial, but how one can devise a tensor metric specifically for a constantly accelerating system while the constancy of the acceleration depends on the intrinsic(spin angular momentum and the longitudinal asymmetry) properties of the mechanical system under investigation. But I'm sure someone will come up with an answer. Basically, it's a metric where the source is a rotating hemispherical type (longitudinally asymmetric) rotor. Of course, nice thing about the linearized theory is that one can get a glimpse of the strong field regime without actually finding the metric sorely representing the gravitational dipole moment.
The jets from the rotating ultra compact stellar object is just as common as the winds and storms in the earth environment. And the matters ejected from the poles can take a long route to come back to the center by following the gravito magnetic force lines. Those matters in their transit toward the center of the rotating stellar object form dark matter halo in the surrounding space and the gravitational lensing becomes a natural consequence of it. It is surprising that the dark matters are actually found by studying the bullet clusters colliding with the stationary galaxy.
Regarding the bullet cluster, if a small galactic system has started with the initial condition in such a way that it has a longitudinally asymmetric configuration with non zero spin angular momentum, the cluster will run in one direction accelerating as predicted by dipole gravity. As the longitudinal asymmetricity flattens out as time goes by, due to many possible reasons, the constancy of the velocity will be set in and it becomes a bullet cluster.
The major development in the process of publishing the blog was the finding of the sign error in the Lens-Thirring force. After the correction, it flood gated all the subsequent understandings, ie, the consistent gravito magnetic force lines, the dark matter halo and the details of the intricate black hole jet engine mechanism.
Best Regards,
Eue J Jeong
==Answer to the question regarding the covariance of dipole gravity prepared earlier==
It looks like this is a common question in the minds of astro physicists as I have encountered more than several times. When Einstein's field equation is linearized, the individual terms are not by themselves covariant. For example, Newtonian (monopole) gravity will not be covariant by itself. Neither is dipole gravity. While they are parts of the solution to Einstein's field equation, the exact validity of it will be diminished substantially as the system goes into the extreme relativistic regime.
However, one can assume with great confidence that the major property of either monopole or dipole gravity will not change drastically as the system develops into the strong field regime. Black hole's gravity potential is different from the linearized weak field monopole(Newtonian) gravity, only in the way its functional variation over the close distances. The fundamental radial character of the monopole gravity force will not change. For example, the monopole gravity will not change suddenly into the dipole gravity just because the system goes into the strong field regime.
So, one can see that dipole gravity is a totally new entity. Its weak field limit property will not change into something else(other than dipole gravity itself) even if the system goes to the extreme relativistic regime.
One can see that there can be two different ways to perform research in general relativity to discover a new physics. One is trying to find a totally new metric tensor that may reveal some type of new physics in general relativity, which is the way most of the gravitational physicists are focused into these days. The other method is to find an actual mechanical system that can be calculable in the weak field limit of general relativity, which is presented in the theory of dipole gravity as well as in the quadrupole gravitational radiation research, the path of which is limited and has not been sought by many physicists. While some type of metric tensors that have been found may not represent the actual universe, the linearized weak field solution found directly from the mechanical system will represent a part of the actual universe at least in the regime of the weakly gravitating source.
PS; If we look back at the development of general relativity, it is not hard to see that dipole gravity is the true crown jewel of general relativity. Because the first term from the linearized theory which is the monopole(Newtonian) gravity was a totally expected one that can not surprise anybody and the third term which is the radiative type of gravitational quadruple moment is two orders of (v/c) magnitude weaker than the monopole gravity, which makes it extremely difficult to detect its effect. And none of these two known terms of gravitation seems to explain the most prominent cosmological problems of today, namely, the jets and the dark matter problem.
The second term in the linearized theory which is the dipole gravity was a totally unexpected one since it doesn't exist in the context of the classical gravitational physics. And it was not obvious if it does exist and meaningful within general relativity either, so it was generally considered non existent and that the dipole term in general relativity was considered physically meaningless, although many hints were there suggesting that it could exist and be real. For example, Lens-Thirring force should have been taken more seriously because it carries the signature of dipole gravity. And also, since acceleration of mass creates gravitational field, according to the equivalence principle, the gravitational field from the rotating sphere should have been looked at more carefully.
Thursday, June 14, 2007
Pioneer 10/11 Anomaly
The anomalous Pioneer 10/11 acceleration (8.74 +/- 1.33) * 10^-8 cm/s^2 has been reported. For more info, visit http://www.planetary.org/programs/projects/pioneer_anomaly/ .
The acceleration of the Earth in its orbit is 0.593 cm/s^2 on average (1 AU)*(2*pi/yr)^2 making this anomalous acceleration 1.5*10^-7 of that.
However, Pioneer 10 was 67 AU from the Sun in 1997, when its mission was downgraded to a sort of background status, and Pioneer 11 was 40 AU from the Sun when contact with it was lost in 1995. This means that the anomalous acceleration is ~10^-4 of the Sun's acceleration of them at that distance.
Finally, it is noted that calculated nongravitational effects, such as radiation reaction from the spacecraft's radio transmissions and the glow of the RTG's, are not much smaller than the anomalous acceleration itself, suggesting that one may have to model such effects more carefully.
Also, there are no similar effects reported for the Voyager spacecraft, so these may be due to some quirk of the Pioneers.
The following is a quote from the report from NASA at JPL and LANL.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dispassionately, the most likely cause of the anomalous acceleration of the Pioneer spacecraft is on-board systematics, but the smoking gun has not yet been found. The only other possibility is the existence of new physics. This dichotomy represents a healthy win-win situation because either one of these two explanations for the Pioneer anomaly would constitute an extremely important discovery. (Author Slava Turyshev and John Anderson are at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena and Michael Martin Nieto at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, US)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
One possible explanation of this anomaly may be found within the theory of dipole gravity. Since the rotating parabolic antenna of Pioneer represents a dipole gravity rotor, the observed additional acceleration toward the sun can be explained if the antenna is focused toward the sun which means the wider (open) side of the parabola faces the sun. And Pioneer is reported to be spinning at 14.1 sec per revolution which makes it spinning at 4.25 rpm. However, since the effect was not observed from Voyager as prominently(if at all) as it was observed from Pioneer, this may still be an open question.
If Voyager has different mechanical parameter (it also has parabolic antenna) compared to that of Pioneer in such a way that the dipole gravity effect is minimal (for example, the spinning rate is lower and it has more longitudinal axially symmetric configuration), then the mystery could be resolved. For this purpose, the detailed mechanical configuration including the rate of the spin rotation for both Pioneer and Voyager may be needed. This data may be found in the detailed original engineering design in terms of the mass distributions inside the craft.
In the mean time, the following information has been available which can be very significant.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Is the same effect seen with the Voyager spacecraft?
The Pioneers are spin-stabilized spacecraft. The Voyagers are three-axis stabilized craft that fire thrusters to maintain their orientation in space or to slew around and point their instruments. Those thruster firings would introduce uncertainties in the tracking data that would overwhelm any effect as small as that occurring with Pioneer.
This difference in the way the spacecraft are stabilized actually is one of the reasons the Pioneer data are so important and unique. Most current spacecraft are three-axis stabilized, not spin stabilized.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
If the above information is true, in the three-axis stabilized spacecraft case, the anomalous effect would have been automatically canceled or diluted, because of the continuous adjustment of the orientation of the craft. However, in the case of the spin-stabilized craft, the dipole gravity effect will not be corrected which will make the effect prominently visible.
The following information is exactly what can be expected from a dipole gravity rotor placed in the empty space.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What really puzzles scientists, Turyshev said, is that the anomaly is constant with respect to time and distance from about 1 1/2 billion miles away from the sun to about 6 1/2 billion miles out. The anomalous behavior has been observed in other deep space vehicles such as Voyager and Ullyses.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The magnitude of anomaly seems larger than one would expect from a spin rotation of 4.25 rpm regardless of the size of the rotor. But the exact mechanical configuration of the craft is not yet available at the moment. And there is an uncertainty on the average distance and the amount of the mass of the universe which are not well defined relative to the location of the dipole gravity rotor. So, in case a terrestrial experiment is planned for the second confirmation, the Pioneer data will make a good starting point.
In a sense, the alternative experiment that has been proposed for the test of dipole gravity in the page http://dipoleantigravity.blogspot.com/2007/04/alternative-method-of-detecting-dipole.html may have already been done in the space without our knowledge.
Sunday, June 10, 2007
Dipole Gravity and The Big Bang Cosmology
However, as I mentioned in the digression page, it must be emphasized that the exact physical nature of the neutrinos, which are the most mysterious particles in elementary particle physics today, is still controversial, although there is a great chance that they are tachyons. And such assumption doesn't seem to contradict the nature of dipole gravity, instead it helps understanding the cause of the gravity in general. Furthermore, the number of such supporting empirical evidences seems to be growing.
If neutrinos are tachyons, the homogeneity and the isotropy of the universe will be guaranteed at any time in the past and in the future. One doesn't have to worry about if some globular clusters may be older than the age of the universe predicted by the big bang theory.
The reason for the continuous expansion of the universe may be answered if neutrinos are magnetic monopoles themselves as well. It also explains the missing dark energy problem. Will there be final crunch after all these expansions? No one will be able to tell for sure at the moment. We are not certainly in the stage of science being able to contemplate any possibility after the complete expansion of the universe, if there is such a thing as complete expansion.
One thing that can be stated for sure is that there are stages of development of science where certain conjectures can be made on certain questions of the nature. Since no one survived to tell what happened at the time of big bang, most of the features of the theory must be categorized as speculations.
Our visible part of the universe may be expanding but no one knows what is happening to the other invisible part of the universe. So, our ability to foretell the mechanism of the universe is severely limited by our own limitations. As our science progresses to the higher level to be able to physically reach far out side of our own galaxy, our ability to predict the future of the universe will grow as well and become more reliable.
Monday, June 4, 2007
Response to Email Letter from Prof. McGaugh
From: "Stacy McGaugh" (ssm@astro.umd.edu)
To: "ejeong" (ejeong1@sbcglobal.net)
Sent: Wednesday, May 23, 2007 5:49 PM
Subject: Re: Dark Matter is Real
> Yes, it is well known that in MOND there must be more mass than meets the
> eye (about a factor of two, presumably in some mundane baryonic form).
> The recent cluster press releases merely confirm this; they don't shed any
> light on the nature of the unseen mass (baryonic or non-baryonic) which
> makes all the difference.
> Professor Stacy McGaugh
> Department of Astronomy ssm@astro.umd.edu
I think the whole matter will eventually boil down to the priority issue. We haven't exhausted the known theory of gravitation, ie, general relativity. It looks like there are plenty of rooms for the dark matter problem to be taken care of within general relativity without the fundamental destruction of the existing Newtonian mechanics.
That's a humongous assumption. Occam's razor makes it a little bit hard for us to take it in.
Dipole gravity also demands the overhaul of Newtonian mechanics but not in such an arbitrary way. There is a clear cut path to the revision dictated by general relativity.
There is no ad hoc assumption in dipole gravity. It is general relativity itself.
Does MOND predict jets and provide the elaborate jet engine mechanism also? I don't think so. Does it provide any remote clues to the mechanism of creating the macroscopic wormhole, the ultimate method of space travel? No.
I don't know why anyone would want to stick to MOND after the revelation of dipole gravity other than based purely on the sentimental values, which scientists must avoid.
EJJ
Wednesday, May 23, 2007
Occam's Razor
"One should not increase, beyond what is necessary, the number of entities required to explain anything"
Occam's razor is a logical principle attributed to the medieval philosopher William of Occam (or Ockham). The principle states that one should not make more assumptions than the minimum needed. This principle is often called the principle of parsimony. It underlies all scientific modelling and theory building. It admonishes us to choose from a set of otherwise equivalent models of a given phenomenon the simplest one. In any given model, Occam's razor helps us to "shave off" those concepts, variables or constructs that are not really needed to explain the phenomenon. By doing that, developing the model will become much easier, and there is less chance of introducing inconsistencies, ambiguities and redundancies.
Though the principle may seem rather trivial, it is essential for model building because of what is known as the "under determination of theories by data". For a given set of observations or data, there is always an infinite number of possible models explaining those same data. This is because a model normally represents an infinite number of possible cases, of which the observed cases are only a finite subset. The non-observed cases are inferred by postulating general rules covering both actual and potential observations.
For example, through two data points in a diagram you can always draw a straight line, and induce that all further observations will lie on that line. However, you could also draw an infinite variety of the most complicated curves passing through those same two points, and these curves would fit the empirical data just as well. Only Occam's razor would in this case guide you in choosing the "straight" (i.e. linear) relation as best candidate model. A similar reasoning can be made for n data points lying in any kind of distribution.
Occam's razor is especially important for universal models such as the ones developed in General Systems Theory, mathematics or philosophy, because there the subject domain is of an unlimited complexity. If one starts with too complicated foundations for a theory that potentially encompasses the universe, the chances of getting any manageable model are very slim indeed. Moreover, the principle is sometimes the only remaining guideline when entering domains of such a high level of abstraction that no concrete tests or observations can decide between rival models. In mathematical modelling of systems, the principle can be made more concrete in the form of the principle of uncertainty maximization: from your data, induce that model which minimizes the number of additional assumptions.
This principle is part of epistemology, and can be motivated by the requirement of maximal simplicity of cognitive models. However, its significance might be extended to metaphysics if it is interpreted as saying that simpler models are more likely to be correct than complex ones, in other words, that "nature" prefers simplicity.
It will be awfully redundant at this point to reiterate that the theory of dipole gravity doesn't have any assumptions other than the ones general relativity is based on itself. With such a minimal number of assumptions, the number of areas of cosmological problems it touches and provides answers are truly remarkable. The only way it can be wrong is if and only if general relativity is wrong. This perspective gives us the compelling reason to test the predictions of dipole gravity in the terrestrial experiment as soon as possible.
http://dipoleantigravity.blogspot.com/2007/04/alternative-method-of-detecting-dipole.html
Monday, May 21, 2007
Further Digression on the Mechanical Universe
The topic here is still about the tachyonic neutrinos. For the case of the gravitational phenomena, we strictly confined our focus on the kinematic elastic interaction of the tachyonic neutrinos with the baryonic matter particles. However, in this article we will be focusing on the non-kinematic interaction with tachyonic neutrinos. This interaction would not be totally kinematic in the sense that there is a weak interaction effect between the neutrinos and the electrons, muons and tauons(leptons). This is not a high energy interaction either because there are no new particles generated from it as in the case of the deep inelastic scattering interactions. It is not exactly like the billiard ball style collision since there is still finite distance that the interaction can be effective even though there maybe no direct contact between the particles involved. And also, there can be a vector effect like in the case of the electrons traveling in the magnetic field environment. So the effective cross section can be much larger than the case of the kinematic elastic collision. For example, there are speculations that neutrinos may be magnetic monopoles themselves, although not confirmed, if that is the case, the fast moving magnetic monopole will create circular electric field along their path exactly like moving electron creates the magnetic field around it. So the electrons can be affected by the fast moving neutrinos relatively long distance from their path which will make the interaction cross section very large. When there are so many of the fast moving tachyonic neutrinos, the space will be like a bubble bath of electric field popping in and out of them barely managed to cancel each other in the space to avoid the creation of the net electric field in the local space time by virtue of their homogeneous presence and the total isotropicity of their motion.
The situation we are going to imagine in this picture is a single hydrogen atom bombarded by the etheric tachyonic neutrinos. The proton will largely be able to maintain its position because of its larger mass compared to the electron although still its precise position will not be absolutely determined depending on the strength of the cross sections involved. However, the position of the electron will be very uncertain. If the tachyonic neutrinos have enough energy, number density and the strong enough cross section, they will collectively be able to manage to disturb the electron's position frequently and strongly enough to it make it separated from the proton to maintain the Bohr radius. Despite the extremely small physical size of the electrons, the stronger weak interaction coefficient compared to that of the kinematic interaction will be enough to make the electron afloat from the proton by the amount of Bohr radius in the ground state. So, if this is the case, the Planck constant h becomes the function of the number density, the mean velocity and the weak interaction cross section between the tachyonic neutrinos and the elementary particles.
The uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics is caused by this statistical nature of the background tachyonic neutrinos interacting with the elementary particles. For example, quantum mechanics predicts that a particle placed in the space with the initial velocity V=0 at the origin of the coordinate x=0 has less and less chance to be found at the same place as time goes by. This is a clear violation of Newtonian mechanics. It only means that there must be some particles causing this uncertainty to the elementary particles without disturbing the statistical overall average momentum and the position of the particle. This shows the key properties of the background particles, ie, their flux must be isotropic and homogeneous. So, even if the statistical effect is fully applied, the overall averaged initial location and the momentum should be the same. The question where the electron is after a while at the time t=to has no meaning in quantum mechanics. We simply don't know. The most probable location where the electron will be found is still at x=0 but the probability to find it there will be spread out so thinly throughout the space that it would become meaningless to ask where the electron is exactly located at. In the space where tachyonic neutrinos are prevalent, this is exactly what will happen to the elementary particles like electrons.
Now we see how the two phenomena, gravitation and quantum mechanics, seemingly unrelated to each other have the same origin. All the predictions of quantum mechanics will be valid, only difference is that we know now it's an excellent phenomenology because while it worked and predicted the nature so well, still it didn't provide the clear answer to the mechanically inquisitive human mind. As Einstein put it "God doesn't play dice game". We humans want to know in mechanical terms why it is working if something really works and what is behind it. "Trust me it worked million times in the past and it should work in the future, so no more questions to the validity of it" would not be enough.
So, there is a possibility that inside the stars where the tachyonic neutrinos can not penetrate with enough numbers, the Bohr radius of the hydrogen atoms could be much smaller than it would be in the open space (assuming that they(hydrogen atoms) could manage to stay as individual atoms inside the stars) because there will be much less frequency of the tachyonic neutrinos disturbing the electron's position to make it stay far enough distance from the proton to maintain the same Bohr radius as they were in the open space. Since light cannot penetrate the bulk object, it will be hard to tell if the light that we detect belongs to the quanta that generated from the core of the stars. Most of the visible light we observe will be coming from the surface of the stars. So the observation of those lights will not provide the clear answer to this question.
Another interesting question would be what would happen if all the tachyonic neutrinos simply disappear. All the matters and stars will collapse to become like tiny pieces of dots in the universe and the energy generated from it will be so large that the big bang would be an insignificant event compared to it. On the other hand, there will be no gravity so the universe will become like a soup of murky cloud, dark, dull and lifeless and meaningless presence of emptiness all over the space if there is such a thing that can be called "space" left anymore.
In fact, the meaning of the space itself would become vague and uncertain because the pressure of the tachyonic gas seems to define the space itself as we observe it, as much as the pressurized air molecules inside the balloon defines the space of the balloon itself. In fact, it can be seen that the tachyonic neutrinos are the main building blocks of the universe instead of the material particles we observe and live in them. In a sense, the material particles(stars, galaxies, etc etc) are like the sea sponges floating under the deep sea water of the tachyonic neutrino gases spread through out the universe.
Wednesday, May 16, 2007
Digression on the Cause of Gravity
The nature of the dipole gravity force is peculiar in the sense that it critically depends on the bulk geometrical shape of the object. This aspect was not clear from the example of Newtonian gravity since the monopole gravity is not sensitive to the geometrical shape of the object at all. Also all the elementary particles are assumed to have the same geometrical shape like a sphere.
This peculiar aspect of dipole gravity makes one wonder if quantisation of gravity is the right way to understand gravity because gravity looks like more of a bulk phenomenon than the quantum phenomenon.
So, the findings that the rotational motion creates the longitudinally asymmetric gravitational field around the rotating object like a hemisphere, cone etc may provide some additional clues.
In effect, the asymmetrical rotor must be acting like a propeller, but in what way?
Let's assume for the sake of argument that the universe is filled with tachyonic neutrinos. I published the paper titled "Neutrinos must be Tachyons" in the llnl archive which has a very good empirical evidence that it must be the case (http://www.tachyonics.com/neutrino.pdf). One should read it to see how strong the case is for it. It must be realized that there are as many neutrinos as the number of electrons and protons in the universe because the weak decay produces one in each and every cases of its interactions.
What people have not been asking is "where have those astronomical number of the neutrinos gone?" There are too many of them and the elementary particles don't simply disappear, yet, no one seems to be bothered by their apparent absence from our daily perspective of the universe.
If they are not tachyonic, they must be hanging around some part of the universe gravitating to form some kind of observable macroscopic object, which has never been found. If neutrinos are tachyonic, the case for which is very strong at the moment, they must be traveling inside of our universe incessantly. So, it is quite probable that the universe is filled with tachyonic gas like the atomic molecular gas filled up inside a balloon which may be composed of many different kinds of neutrinos if not one. After all, these tachyonic gas may form the aether itself that the light uses it as a medium to propagate like the sound wave propagates through the pressurized air filled earth surface. When Michelson and Morley performed their experiments, their major assumption was to find the solid or materialistic form of the aether not like the superluminal kind we are talking about. The aether drag effect Michelson and Morley expected to find will not exist if the aether was formed by superluminal object like tachyonic neutrinos. Furthermore, to reinforce this proposition, neutrinos are not totally immune from the light particles since they are related to each other by the electro-weak interactions. Photons and neutrinos are family members within the framework of electro-weak theory. So like in the case of the sound wave propagating through the air molecules, the compression and the relaxation of the local density of the tachyonic neutrinos generates the ripple effect to carry the light through the long distances.
The neutrinos rarely if ever interact with matters. At least that's what has been understood regarding neutrinos. However, this statement may not be entirely correct. Most of the metals and rocks are free to pass for neutrinos. However, there can be substantial kinematic non zero cross sections with baryonic matters when they are densely populated inside to form a star. The purely kinematic interaction like elastic head on collision will not produce the high energy producing strong interaction effect. So, there is really no way of knowing how the low energy neutrinos are interacting with ordinary matters. But such an elastic interaction can be expected to exist and it could be much more frequent and common than one would expect. It's basically like two billiard balls of different size collide and then bounce off from each other. The total energy and the momentum is conserved in this process, ie, the sum of the initial momentum and the energy must be the same as the final sum of the momentum and energy. Besides most of the neutrinos do not have high energy to begin with. The energy equation dictates that the lesser energy the tachyonic particle has, the faster they travel while still satisfying the Lorentz invariance. They behave in a totally different manner compared to the usual matter particles. They are not observable beside the fact that they interact kinematically with baryonic matter inside the dense stars or by the high energy neutrinos generated from the super nova interacting with the baryonic matter in the laboratory experiment.
Therefore, in a way, the core of the dense star forms a "aether vacuum" meaning that there is less and less chance for the tachyonic neutrinos can penetrate into the core of the dense stars. The strength of the aether vacuum depends on the elastic collision cross section and the number density of the tachyonic neutrinos and the average speed of them which will determine the mean relaxation time and also the characteristics of the dense object itself which will be the measure of its own density and also its volume.
So, the gravitational constant G becomes a function of those three physical quantities, ie, the number density, the average speed and the elastic collision cross section of the tachyonic aether particles with the matter.
So, here is the fundamental proposition,
The gravity is caused by the "Tachyonic Neutrino's Aether Vacuum".
Now let's see if this proposition can be consistent with dipole gravity. The rotation of the longitudinally asymmetric object creates asymmetric ether vacuum along the rotation axis, because the larger diameter side has more chance to knock off the tachyonic neutrinos due to its faster tangential velocity thereby creating the higher ether vacuum state compared to the other side where the tip of the dome or the pointed edge of the cone is located while in rotation. So there is a gradient of tachyonic vacuum pressure formed along the longitudinal direction of the asymmetric rotating object.
The lower pressure side is where matters tend to move toward and it becomes the center of gravitation. It is basically the same concept like the air plane propeller except that the tachyonic aether can not be pushed or moved by the blade of the propeller but only by the fast rotating motion of the dense object (until one can find the alternatives which will become the core of the engineering the tachyonic aether in the future).
This is also consistent with the fact that the rotating cylinder does not create dipole gravity.
The inertial effect is caused by the tachyonic neutrino's balancing act to position the object in place from all directions while trying to give it a net momentum. Of course the centrifugal force is a natural consequence of this inertial tendency of the matter in the universe. It doesn't have to require the existence of all the matters in the universe at least in a direct way. However in the process of the creation of all the matters in the universe, there must have been the same number of neutrinos generated as the number of protons in the universe which have become the part of the aether. So, there is certainly a remote relation but not in such a direct way as Mach described.
It also indicates that the empty space is pretty well balanced which means the universe is homogeneous and isotropic in terms of tachyonic neutrino's population and its density. And their fast balancing act is not hard to understand considering their immense speed of travel in the universe.
The Gaussian flux concept of the gravity force line is also consistent with this concept of the tachyonic aether vacuum because of the isotropic presence of the tachyonic neutrinos and their motions. The fundamental law of kinetic theory of gas is that the nature abhors vacuum. It must be filled up and equalize the pressure all over the space and that is also the fundamental reason for all kinds of weather phenomenon on earth.
So, in a sense, cosmology is a weather phenomenon caused by the movement of the tachyonic neutrino gas in the universe. The fast rotating black hole pushes and pulls the tachyonic gas and it produces the jets because of the imbalance and the peculiar formation of the tachyonic gas pressure in the surrounding area of the rotating galactic centers.
It's like each particles are the actors in the theater of the immense universe. They act in such a way their characters are assigned like in the Shakespearean play. Tachyonic particles have to play their role as much as baryonic matter particles play their roles.
The reason for the unusual weakness of the gravitational interaction compared to other interactions may be attributed to the fact that the kinematic elastic collision cross section of the tachyonic neutrinos with the matter particles is extremely small compared to other interactions.
The Cause of the Flat Rotational Velocity Curves
The fundamental mystery in the dark matter problem is in the flat rotation curve as the distance becomes large from the galactic center.
{courtesy from Dr. Greg Bothun}
Within the framework of the usual dark matter halo hypothesis, if the density of the halo is assumed to be constant, it will not generate the logarithmic potential which is necessary to address the flat rotation curve. If one wants to make up an arbitrary density function to make it fit the rotation curve, one has to explain how the distribution has come about that way. However, if the dark matter halo is made of the continuous cycling flux of the matter ejected by the jets, as predicted by the theory of dipole gravity, the volume density of the dark matter halo will not be constant, instead the flux density will be a constant, because it has the definite source located at the center of the rotating galaxy. The effective gravity potential produced by the dark matter halo can be expressed by
in general form, where ρ(r) represents the density function of the dark matter halo. Since the source of the dark matter halo is coming directly from the jets from the rotating galactic center, the total mass of the matter particles populated within the volume defined by 4 π r^2 times the unit length of r will be the same until the density of the halo diminishes to zero. So, the effective gravity potential within the applicable regime becomes
where M is the sum of the total mass within the volume element 4 π r^2 times the unit length of r. The logarithmic gravitational potential is the typical signature for the flat rotation curve.
The gravitational force within the relatively short distance from the center of the rotating galaxy is dominated by the strong dipole gravity force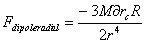
as derived previously, which explains the sharply increasing slope in the rotation curve near the galactic center.
In his prophetic statement, Dr. Greg Bothun writes, quote
"However, it's important to realize that the "dark matter" problem exists only in the context of one known long range force (gravity). Suppose there is another long range force that we are ignorant of. If this is discovered by future physicists then they will look back at this "dark matter" cosmology much the same way we now view the early "geocentric" cosmologies."
How Lense-Thirring force is derived from dipole gravity?
Einstein's Triumphant Legacy
But it was not clear in regard to how that works, in what way and through what kind of mechanism to cause a realistic gravitational field.
The analogy with electro-magnetism certainly failed. Rotating donut shaped object didn't create gravito magnet. Lens-Thirring's force from the rotating spherical shell indicated there is a remnant of the acceleration of the mass induced force near the center of the sphere but the interpretation and the sign of the force were incorrect. The radial component of the force was interpreted as the centrifugal force in accordance with Mach's principle and there was no explanation for the harmonic force along the axis of the rotation. And none of these forces seemed to give any clues to the existing cosmological problems. And it didn't encourage any further investigation into the subject largely because of the horrendous difficulties in analytically calculating all the details of the gravity effect from the circular motion of the spherical object. And the dipole term from the linearized theory was simply interpreted as meaningless and it was declared that there is no such thing as dipole gravitational moment as a physically meaningful entity.
Thus, the question remained a fundamental mystery of general relativity. How the circular motion of the mass manifests itself into a verifiable gravito magnetism?
Even if the rotating frequency and the tangential velocity of the object may be considered crucial to the effect, it was not obvious how it should be incorporated into the final form of the gravito magnetism. The most crucial and final stumbling block may have been Newtonian mechanics itself since there is no such thing as the shift of the center of mass by a fixed definite quantity depending on the speed of the rotational motion in Newtonian mechanics. It simply won't happen. Of course, this can be used to perfectly justify the claim of the non existence of the gravitational dipole moment if and only if one assumes that Newtonian mechanics is the flawless and complete theory of the mechanical universe.
Dipole gravity(gravito magnetism) is a plain and inevitable solution to general relativity that has been sought but eluded the researchers in the field for a long time. Clearly it was not obvious to Einstein himself. But there is no doubt that it is still one of his most triumphant legacies.
He would have been very happy to see the solution of his own theory explaining the mysteries of the universe ranging from the jet phenomena to the dark matter problems which did not emerge as the prominent cosmological problems at his time.
We can learn here the pattern regarding on how the old and new principles of physics exchange and compete to evolve into a new principle to teach us something new. When there is a new principle which is larger and incorporating the old principle, there is a crucial and unique mechanism that shows the clear conflict between the old and new principle at which point one is forced to choose one and thereby face the demands of the modification of the old principle to make it compatible to the new one.
In any circumstances, the final result is that it forces us to abandon certain features of the old principle. This happens in a continuous fashion in the history of mankind and that is how the secret of the nature is continuously made comprehensible.